![[PukiWiki] [PukiWiki]](image/pukiwiki.png)
![[PukiWiki] [PukiWiki]](image/pukiwiki.png)
уААуААуААThe UI of application can be set by the combination of View and ViewGroup.
уААуААуААуГ╗The set of Veiw is ViewGroup.
уААуААуААуГ╗ViewGroup contains two or more View.
уААуААуААуГ╗ViewGroup can be contained in ViewGroup.
уААуААуААуГ╗The layout inherit ViewGroup.
уААуААуААтА╗Refer to the following succession charts for the practical visualization.
уААуААуААуААViewGroup and the succession relation are described as follows.
уААуАА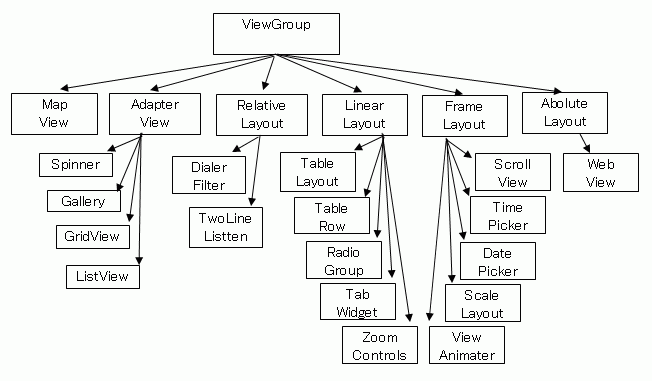
уААуААуААуААTypical View-Groups (layouts) are described as follows.
| тЕа | уААAbsolute layoutуАА | уААThe layout placement which specifies the absolute coordinate.уАА |
| тЕб | уААRelative layoutуАА | уААThe layout placement which specifies the relative coordinate.уАА |
| тЕв | уААLinearуАА layoutуАА | уААHorizontal direction and the vertical direction can be specified. уАА |
| тЕг | уААTableуАА layoutуАА | уААThe table form can be arranged. уАА |
| тЕд | уААFrameуАА layoutуАА | уААOverlapping the VIEW is possible. уАА |
| уААthe othersуАА |
уААуААуААуААуГ╗Layout specified by using [absolute coordinate]
уААуААуААуААуГ╗It became non-recommendation from SDK1.5. я╝ИBecause this layout cannot support multiple devices for different screen sizes.я╝Й
уААуААуАА уААуАА
уААуАА
уААуААуААя╜Мя╜Бя╜Щя╜Пя╜Хя╜Ф_я╜ШуАА
уААуААуААя╜Мя╜Бя╜Щя╜Пя╜Хя╜Ф_я╜ЩуАА
уААуААуААя╜Мя╜Бя╜Щя╜Пя╜Хя╜Ф_я╜Чя╜Йя╜Дя╜Фя╜И
уААуААуААя╜Мя╜Бя╜Щя╜Пя╜Хя╜Ф_я╜Ия╜Ея╜Йя╜Зя╜Ия╜Ф
уААуААуААя╜Жя╜Йя╜Мя╜М_я╜Ря╜Бя╜Тя╜Ея╜Оя╜Ф is MAX size. я╜Чя╜Тя╜Бя╜Р_я╜Гя╜Пя╜Оя╜Фя╜Ея╜Оя╜Ф is minimum size.
уААуААуААуААLayout which specify the relative position of widget. Can be specified placed in the top or bottom.
уААуААуАА

уААуААуААуАМхЯ║ц║ЦуБоф╜Нч╜оуВТхдЙцЫ┤уБЩуВМуБ░уАБуБЭуВМуБлф╝┤уБДуБ╗уБЛуБоуВжуВгуВ╕уВзуГГуГИуВВшЗкхЛХчЪДуБлф╜Нч╜оуБМшк┐цХ┤уБзуБНуВЛуАНуАМцЦЬуВБуВДхЖЖх╜вуБлуВВщЕНч╜оуБМхПпшГ╜уАНуБиуБДуБЖуГбуГкуГГуГИуБМуБВуВЛф╕АцЦ╣уАБ
уААуААуААуАМц░Чш╗╜уБлуВжуВгуВ╕уВзуГГуГИуВТш┐╜хКауГ╗хЙКщЩдуБзуБНуБкуБДуАНуАБуАМуБйуБоуВИуБЖуБлуГкуГмуГ╝уВ╖уГзуГ│уБХуБЫуБжуБДуВЛуБЛхИЖуБЛуВЙуБкуБПуБкуБгуБжуБЧуБ╛уБЖуАНуБиуБДуБЖчВ╣уБМуГЗуГбуГкуГГуГИуАВ
уААуААуААуААLiner Layout is the layout which arrange widgets at straight vertical or horizontal.
уААуААуАА уААуААуААуААуААуААуАА
уААуААуААуААуААуААуАА
уААуААуААThis layout can arranged widget in a tabular.
уААуААуАА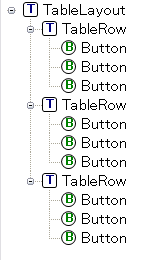 уААуААуААуАА
уААуААуААуАА
уААуААуААуААуААуААуААOutlineуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААScreen
уААуААуААуААхПВшАГя╝ЪуГЬуВ┐уГ│уБоуГмуВдуВвуВжуГИ
уААуААуААуААhttp://www.javadrive.jp/android/xml_layout/index7.html
уААуААуААуААхПВшАГя╝ЪчФ╗щЭвуБоф╜ЬуВКцЦ╣
уААуААуААуААhttp://www.techfirm.co.jp/lab/android/view.html
уААуААуААуААхПВшАГя╝ЪAndroid Developer
уААуААуААуААhttp://www.techdoctranslator.com/android/guide/ui/declaring-layout
уААуААуААуААхПВшАГя╝Ъцмбф╕Цф╗гхЙ╡щАацйЯцзЛ
уААуААуААуААFrame layout is easy to use when stacking the View.
уААуААуААуААFor example, when overlaying images is available.
уААуААуАА уААуААуААуАА
уААуААуААуАА
уААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААOutlineуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААуААScreen
уААуААуАА
уААуААуААIf you want to set half-and-half to buttons layout ,
уААуААуААUse "LinearLayout",and assign 0 to "layout_width",and assign 1 to "weight".
уААуААExample of layout.xml
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/linearLayout1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="хЙНуБ╕"
android:id="@+id/Button01"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
</Button>
<Button
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="цмбуБ╕"
android:id="@+id/Button02"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true">
</Button>
</LinearLayout>
уААуААуААхПВшАГ - Android Wiki
уААуААуААуГ╗я╜Оя╜Ея╜Шя╜Фя╝жя╜Пя╜Шя╜Хя╜Уя╝дя╜Пя╜Чя╜О - уГХуВйуГ╝уВлуВ╣уБМф╕ЛцЦ╣хРСуБлщБ╖чз╗уБЧуБЯцЩВуБощБ╖чз╗хЕИViewуВТхоЪч╛й
уААуААуААуГ╗я╜Ря╜Бя╜Дя╜Дя╜Йя╜Оя╜З - ф╕Кф╕Лх╖жхП│уБоуГСуГЗуВгуГ│уВ░уВТшинхоЪ
уААуААуААуГ╗я╜Уя╜Гя╜Тя╜Пя╜Мя╜Мя╜Вя╜Бя╜Тя╝бя╜Мя╜Чя╜Бя╜Щя╜Уя╝дя╜Тя╜Бя╜Чя╝╢я╜Ея╜Тя╜Фя╜Йя╜Гя╜Бя╜Мя╝┤я╜Тя╜Бя╜Гя╜Л - уВ╣уВпуГнуГ╝уГлуГРуГ╝уВТшбичд║уБЩуВЛуБЛуБйуБЖуБЛ
уААуААуААхПВшАГ - Android Wiki
уААуАА
уААуААуААUnit that can be used by layout
| px | уААpixelsуАА |
| dp | уААDensity Independent PixelsуАА |
| sp | уААScale Independent PixelsуАА |
| mm | уААmillimeter |
| pt | уААPointуАА |
| in | уААInchуАА |
уААуААуААThe Horizontal screen, Use "Layout-land" Folder.
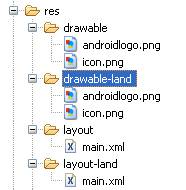
уААуААBack